Sahyog – Alzheimer’s Caregiver App
Sahyog App – UX Case Study
Empowering Indian families in their journey of caregiving for Alzheimer’s
Designing an Educational Resource for Neurodivergent Care: Enhancing Family Awareness and Caregiving Practices for Alzheimer’s
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease affects not just patients but also the family caregivers who support them daily. In India, the lack of awareness and guidance leaves many caregivers feeling unprepared and isolated. This case study explores Sahyog - a digital resource designed to empower caregivers through pre-diagnosis alert tests, interactive learning, community support, and nearby care center locators. Usability testing showed Sahyog boosted confidence, preparedness, and created a safe space for learning and sharing. This project highlights the power of user-centered design in transforming caregiving for sensitive neurodivergent conditions.
Why India?
- India's ageing population is rapidly increasing and by 2050, 20% of its population will be ageing over 60 years, by 20% i mean 14 million people.
- 4 million of people in India are affected by some form of dementia, including Alzheimer’s.
- It's often misunderstood with the symptoms of "normal ageing" rather than a medical condition.
- People find it emotionally unacceptable to send their older parents to a third party caregiver or admitting their parents to some care centre even though if the centers are well equipped.
Problem Statement
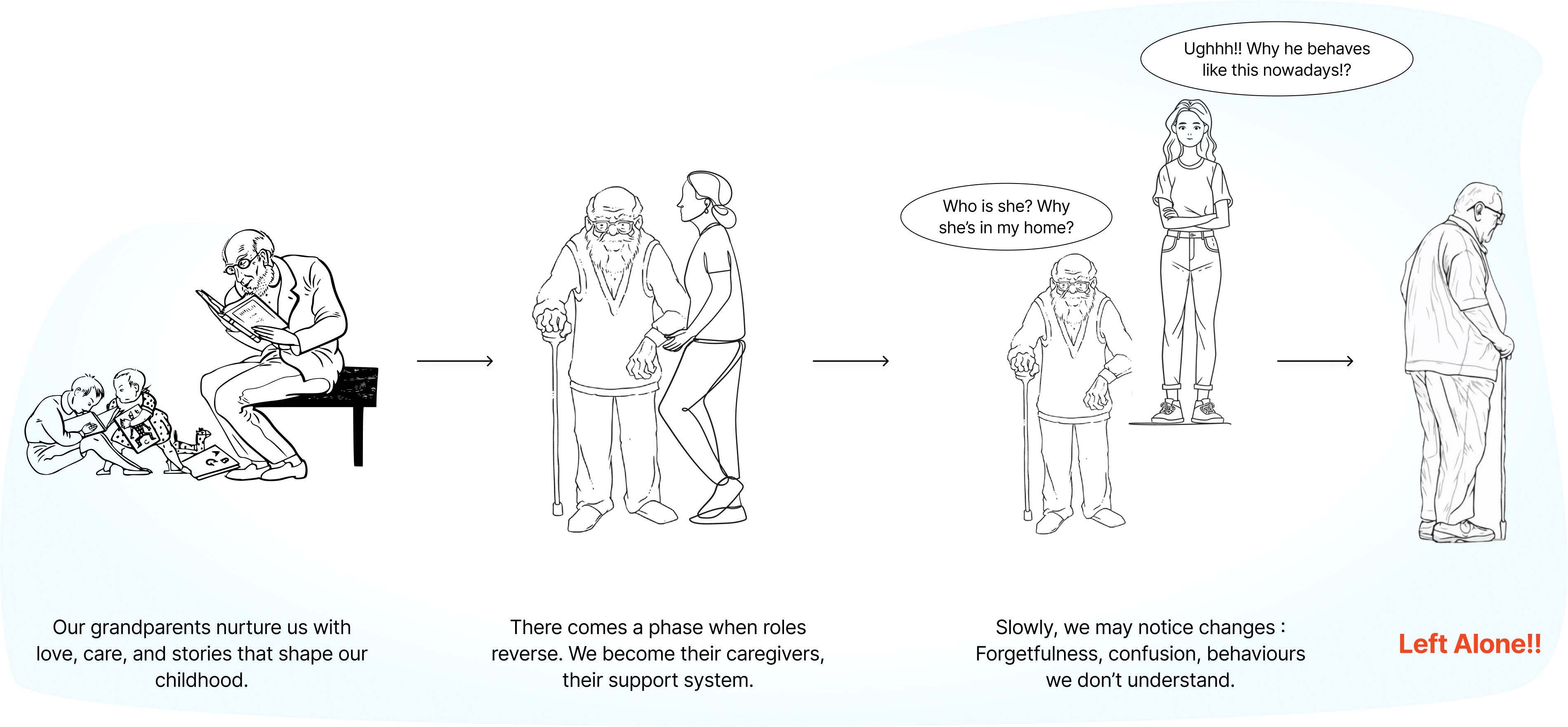
Alzheimer’s doesn’t just steal memories, it disrupts daily life, creates deep dependency, and places an enormous emotional and physical burden on families. In India, where caregiving is seen as a sacred family duty, this challenge is even heavier. Cultural beliefs discourage seeking external help, leaving families to struggle alone, often without the knowledge or support they need. As the disease progresses, so does the stress, leading to breakdowns in both personal and professional lives. This rising gap calls for an accessible, culturally sensitive solution that empowers families with the right information, emotional readiness, and timely access to experts, so they can provide better care without feeling lost or isolated.

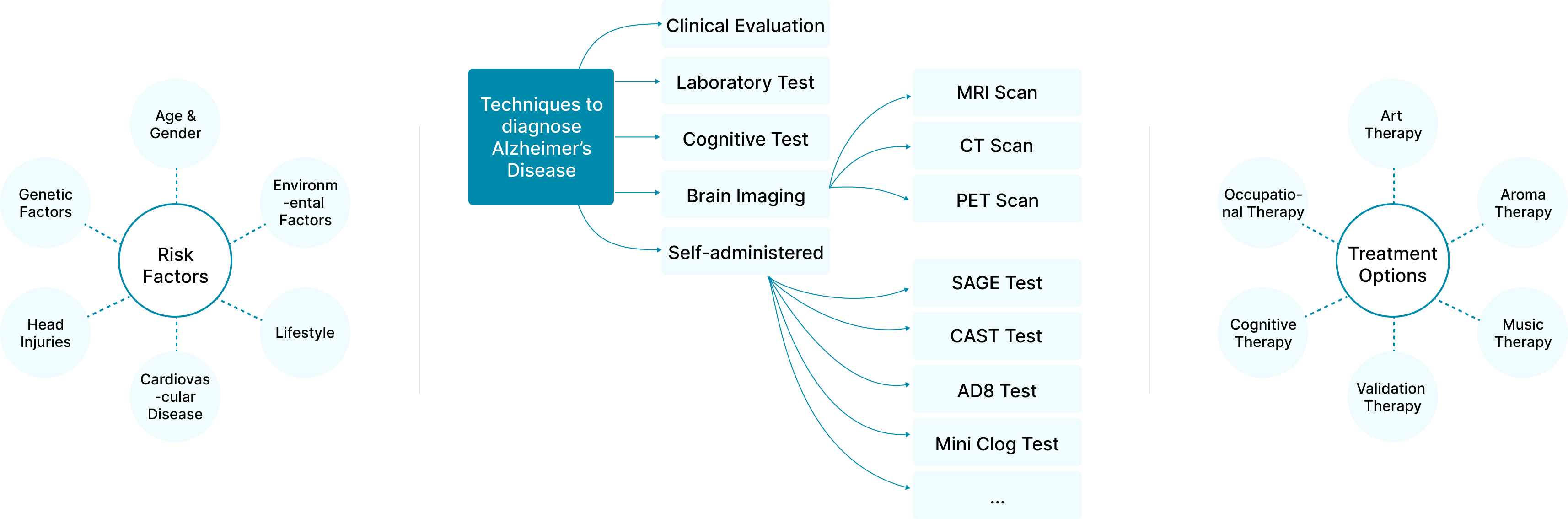
Gaps in Current Educational Approach
Dementia in India faces a massive 90% treatment gap, with only 1 in 10 getting proper care. Widespread lack of awareness fuels stigma, families often dismiss symptoms as mere forgetfulness or label loved ones with words like Bhulakad (forgetful) or Bawla (mad). This deep-rooted misinformation not only delays diagnosis but also breeds shame and neglect within society.
Objective
- Identify gaps and challenges in Alzheimer’s care among families, caregivers, and centers.
- Explore cultural stigmas and their impact on care in Indian society.
- Uncover needs and expectations of caregivers.
- Design a digital solution to educate, support, and connect people.
- Assess how user-centered design can improve caregiving quality and confidence.
Qualitative Interviews & Brainstorming
Family members played a key role as they were in constant contact with Alzheimer’s patients, experiencing the journey alongside them and acting as intermediaries between the patients and professionals.
I wish I could have stayed longer with my grandparents. At one stage in my life, the only conversation I had with them was "Do you remember my name?", "She’s my mother who takes care of you, don’t you remember her?"
I do not trust an outsider at all, what if they leave my parent inside the washroom and forget to get them out. Because today’s generation is so into mobile phones all the time.

Field Visits & Observations
A systematic outreach was conducted to approach elderly care centers in India. A list of centers was compiled, and key contacts were identified through social media and personal networks. Initial contact was made remotely via email and LinkedIn, sharing the research objective, background, and a brief self-introduction.

Using a human-centered Design Thinking approach, the focus remained on solving the right problem by engaging deeply with key stakeholders through online interviews and field visits in India, to understand their challenges, empathize with their experiences, and create a safe space for open sharing.
User Persona
Family members (ages 15-50) living with elderly relatives showing early signs of forgetfulness.

Pain Points
- Lack of basic Alzheimer’s knowledge in families.
- Denial phase delays diagnosis and care.
- No credible, accessible home test options.
- Fragmented caregiving resources in India.
- Caregivers feel isolated and unsupported.
Solution
The key points that were focused and self analyzed:
- How the family caregivers can understand basics of Alzheimer’s through an application?
- How can the features be made reliable enough for them to trust and use?
- How they can get information about caregiving practices through an application?
- How a safe environment can be created on a digital platform where they find it easy to communicate and share experiences?
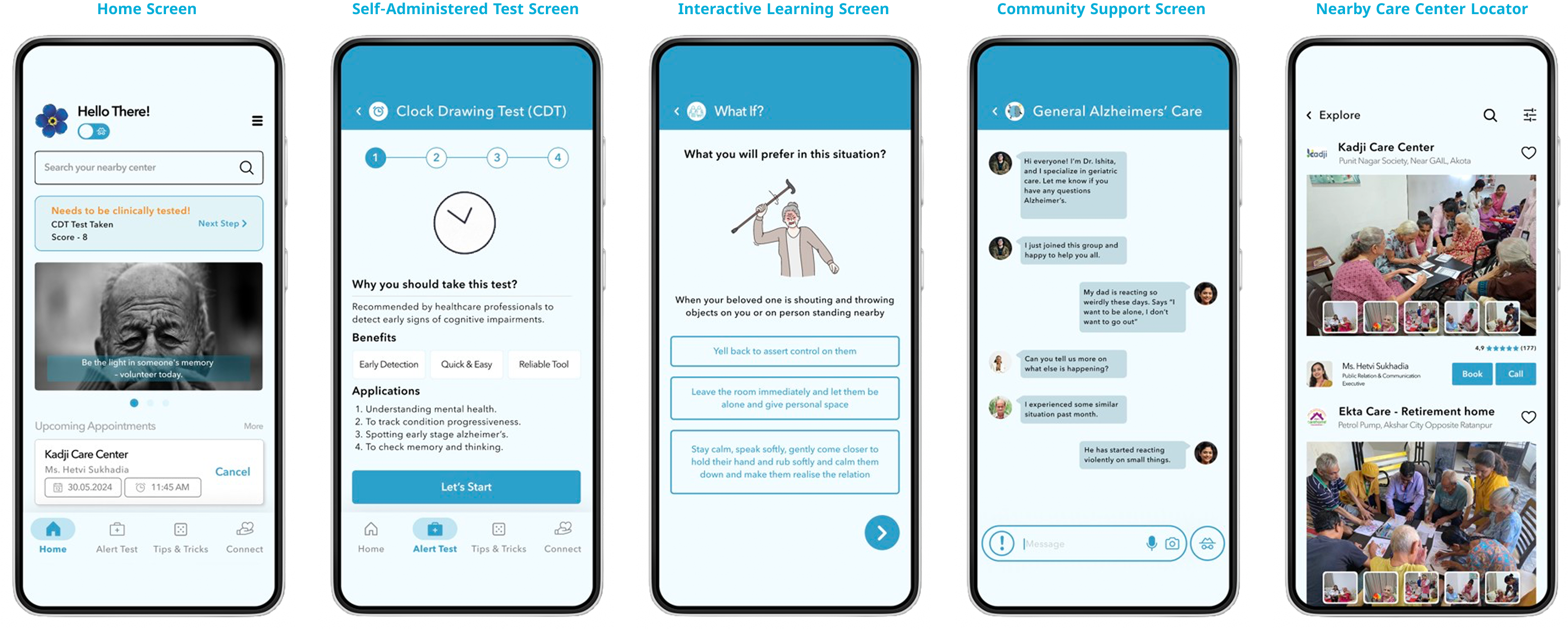
Features & Functionalities proposed:
Pre-Diagnosis Screening Test: A self-assessment tool designed to help families spot early signs of Alzheimer’s at home, with simple step-by-step guides, no clinical help needed. It made existing but lesser-known tests more accessible to those caring for loved ones. Each test included a clear note encouraging expert consultation, ensuring families use results as guidance, not a final diagnosis.
Community Support: Families shared that certain incidents at home felt embarrassing and isolated them socially. This feature created a safe space where they could share experiences without judgment and find support from others facing similar challenges.
Helpline Support: An all-India toll-free support feature offering quick, professional help in urgent situations, especially for those without easy access to medical resources.
Interactive Learning: Simplified guides to help family caregivers manage daily tasks and handle challenging situations, reducing fear and building confidence for future caregiving needs.
Explore Nearby Centres: Helps family caregivers quickly find Alzheimer’s care centers nearby — addressing the common struggle of locating the right support and making the step from learning to action seamless.
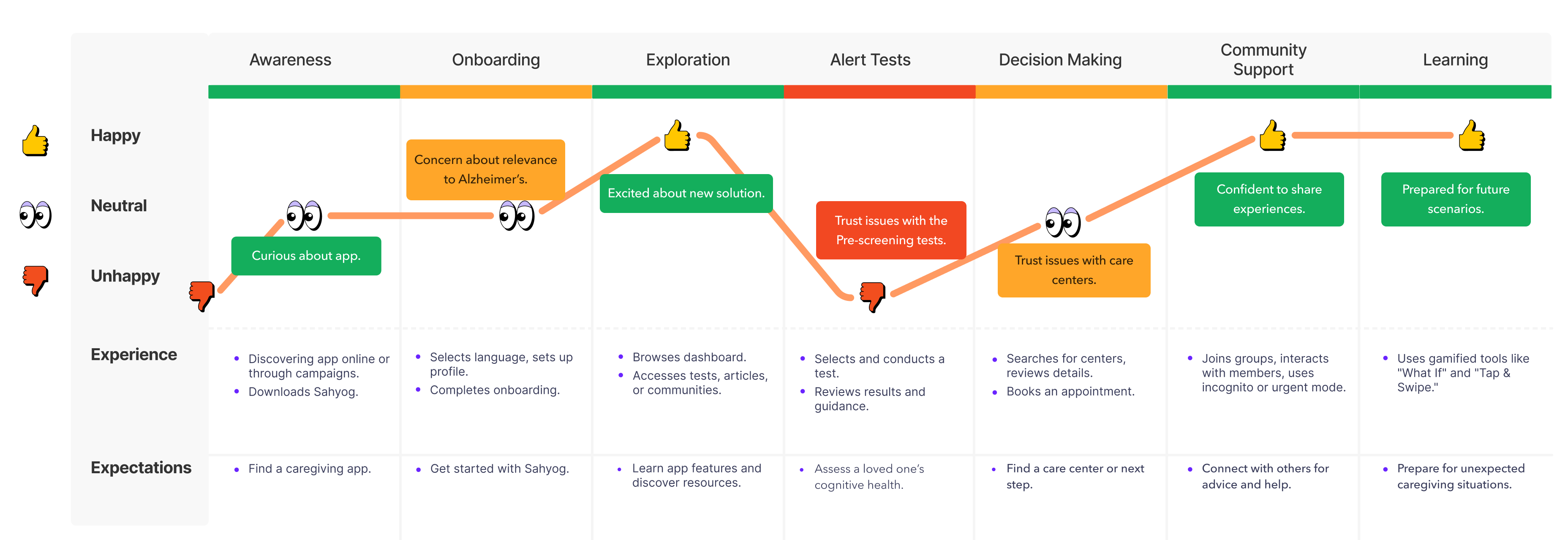
User Journey Mapping
Lo-Fi Prototype & Testing
The paper prototype testing took place with the following criteria was:
- Unstructured moderated usability testing method that was adopted.
- Participants - 5 Family members
- Location - Onsite at Homes
- Time duration - 30 min


Visual Language


Final UI Designs
Prototype
These designs are the result of deep research, iterative thinking, and countless hours of work, to maintain the integrity of my work and protect it from unauthorized use, full prototypes are not publicly accessible.
If you’d like to view them, please reach out - I’d be happy to walk you through them! (karuna.solanki@outlook.com)
Conclusion
“Sahyog bridges the awareness gap and empowers Indian families to provide better Alzheimer’s care at home.”
Through structured learning, credible testing, and a supportive community, Sahyog transforms family caregiving into an informed and confident journey.